Electronic Hazardous Waste (E-Waste)
What is e-waste?
Electronic waste, or “e-waste,” is any unwanted electronic device or cathode ray tube (CRT). In California, e-waste is a universal waste which is a type of hazardous waste. It is hazardous because it may contain materials such as lead and mercury. E-waste is produced by:
Households
Businesses
Government
Industry
Typical e-waste devices include, but are not limited to:
- CRT televisions
- LCD, OLED, and plasma televisions
- LCD monitors, smart displays, and tablets
- Laptops with LCD monitors
- OLED desktop monitors, laptops, and tablets
- Computers, computer monitors, and printers
- VCRs
- Portable DVD players with video screens
- Cell phones and telephones
- Printers
- Radios

The United States is one of the largest e-waste generators in the world
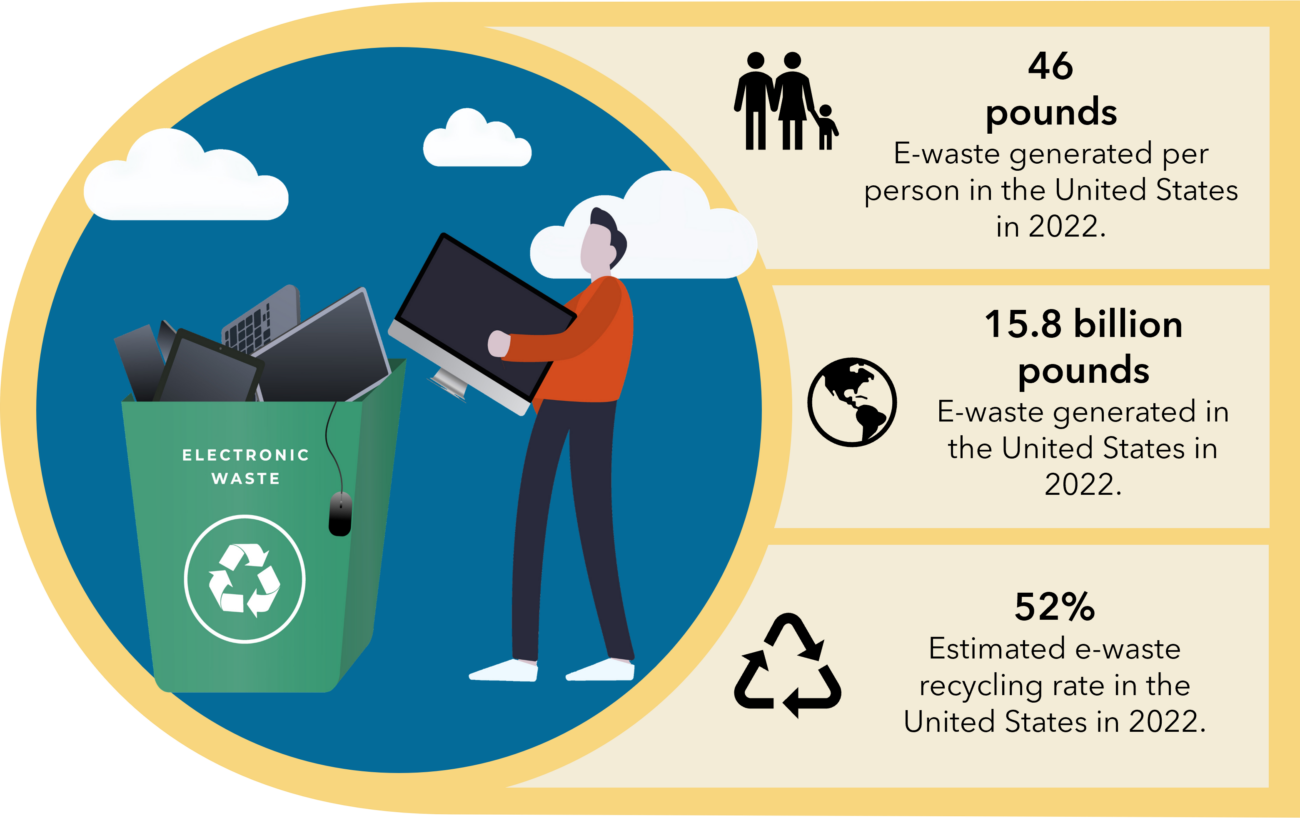
Source: 2024 Global E-Waste Monitor Report – United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR)
Tackling e-waste recycling in California
The electronic device market is wide-ranging. New devices are always coming on the market. It is common for us to replace our old, used electronics with the newest versions and devices. The constant replacement of devices creates a lot of unwanted electronic products. These unwanted electronic products are “e-waste.”
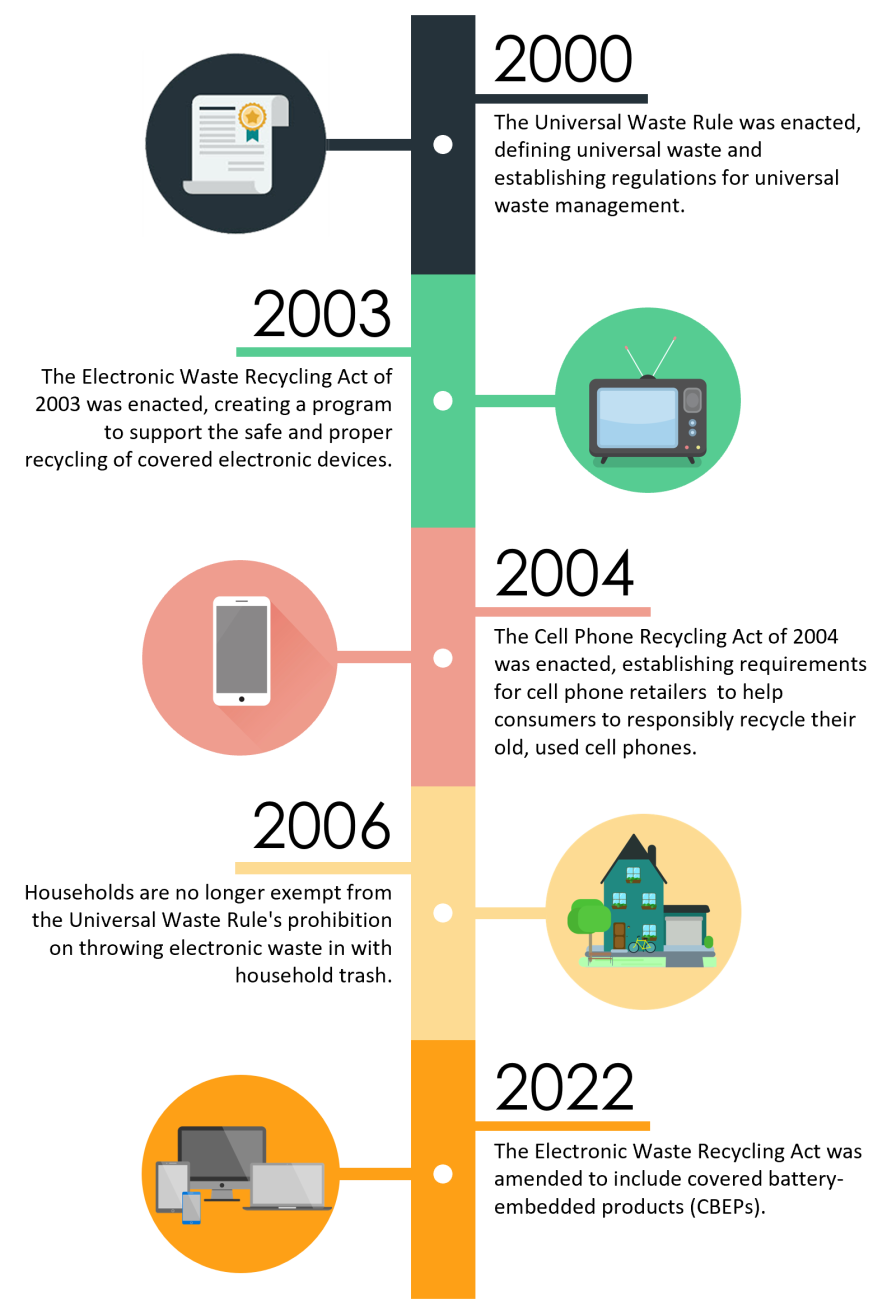
E-waste is a hazardous waste. Disposing of it in landfills may harm both human health and the environment. California passed the Electronic Waste Recycling Act (EWRA) in 2003 to address this e-waste issue. The Act created a program to ensure the safe and responsible disposal of your covered electronic device (CED) waste. CEDs are a type of electronic waste.
For more information about CEDs, refer to our Covered Electronic Devices webpage.
Managing discarded cell phones
Discarded cell phones are a type of electronic waste so you can not discard them in the trash. To encourage recycling, California passed the Cell Phone Recycling Act of 2004. This Act requires:
- cell phone retailers to have a take-back program for a consumer’s used cell phones
- DTSC to publish an estimated cell phone recycling rate every year.
What does this Act mean for you and retailers? Learn more from our Cell Phone Recycling Act of 2004 Fact Sheet.
Note In 2022, the Responsible Battery Recycling Act of 2022 was signed into law. This Act requires retailers of covered batteries to take part in a stewardship program for the collection of covered batteries. Beginning in 2028, this Act will repeal the Cell Phone Recycling Act of 2004.
For more information on the implementation of the Responsible Battery Recycling Act of 2022, visit CalRecycle’s Battery Stewardship webpage.
E-wastes are universal wastes
California considers e-waste as a one of eight types of universal waste. You may see e-waste referred to as “Universal Waste Electronic Devices,” or UWEDs for short. Universal wastes pose a lower immediate risk to people and the environment when managed properly. This allows them to be handled under more relaxed rules compared to hazardous wastes.
Universal waste
Learn about universal waste in California.
Smashing e-waste is illegal
E-wastes contain hazardous materials. You must take them to to an authorized e-waste handler. You can not dispose of e-wastes with your household trash.
If you are not authorized, you cannot smash or destroy e-wastes. These activities could expose you to hazardous dust and debris. Smashing e-waste (and other similar activities) in places such as rage rooms is illegal in California.

The hazard of e-waste in rage rooms
To learn more about what rage rooms are and and why they are hazardous, refer to our The Hazard of Electronic Waste in “Rage Rooms” webpage.
Handling electronic hazardous waste
California considers “e-waste handling” and “e-waste handler” as:
- “E-waste handling” can include the generation, collection, and/or recycling of e-waste. Handling includes hosting collection events.
- “E-waste handler” is a universal waste handler who generates, collects, and/or recycles e-waste in California. E-waste handler includes businesses hosting collection events.
E-waste handlers must follow specific notification, waste management, and reporting requirements. Requirements vary depending on what type of handling activities you perform.
Note Generators are responsible for determining whether their waste is hazardous waste.
Demonstrating e-waste generation, collection, and recycling activities
If you already handle or plan to handle e-waste, you can use our online Universal Waste Electronic Devices (UWED) Notification and Reporting System to file a(n):
- Notice of Intent (NOI) to handle » for generation, collection, and recycling activities
- Annual Report » due February 1 of each year for all facilities, including collection events
- Export Notification
For assistance regarding the notification and/or reporting process, email us at electronicwaste@dtsc.ca.gov.
UWED Notification and Reporting System
File your NOIs, Annual Reports, and Export Notifications.
Are you interested in hosting a collection event?
For more information on hosting a collection event, refer to our collection event guidance document for what you need to do to host a collection event.
Information and resources for e-waste handlers
The links below will provide you with more in-depth information about handler requirements.
Regulating California’s e-waste
DTSC regulates and enforces the hazardous waste control laws and regulations in California. The Department of Resources Recycling and Recovery (CalRecycle) manages the Covered Electronic Waste (CEW) Recycling Program that was established with the Electronic Waste Recycling Act of 2003.
- Electronic Waste Control Law – Health and Safety Code §§ 25214.9 – 25214.10.2
- Electronic Waste Recycling Act of 2003 – Public Resources Code §§ 42460-42486
- Final Regulations for CRT and CRT Glass Disposition Options
 CalRecycle’s CEW Recycling Program
CalRecycle’s CEW Recycling Program
For more information or if you have any questions regarding the CEW Recycling Program, contact CalRecycle at ewaste@calrecycle.ca.gov.
Electronic Waste Recycling Act of 2003
Learn more about the Electronic Waste Recycling Act and the Covered Electronics Waste Program on our E-Waste More Information page.
Do you have unwanted electronic devices you need to dispose of?
Find an e-waste collector or recycler near you!
Additional external resources — Find an e-waste recycler near you!
- GreenerGadgets by Consumer Technology Association
- Call2Recycle
Note DTSC is not responsible for the content of external internet sites.
Outreach materials and frequently asked questions (FAQs)
- Informational letter: CUPA vs. DTSC Inspection Authority
- Informational DTSC workshops and conference presentations:
Promote e-waste recycling with our printable poster!
Print one (or both!) of these posters to inform others about e-waste and help them to locate a recycling location near them!

Click to open and print

Click to open and print
Links for additional e-waste information
- How is California Doing with Recycling Cell Phones?
- How is California Doing with Recycling Rechargeable Batteries?
- CalRecycle’s e-waste webpage: Electronic Product Management
External resources
We have compiled this list of links to external webpages that contain information that may be of interest. DTSC is not responsible for the content of external internet sites.
- Google’s Sustainability blog: What should we do with old electronics?
- 60 Minutes: America’s Toxic Electronic Waste As It Is Illegally Shipped to Become China’s Dirty Secret
- Basel Action Network: a non-governmental organization focused on international trade of hazardous waste
Contact us
For questions regarding e-waste: electronicwaste@dtsc.ca.gov
For general questions, contact the Regulatory Assistance Office:
1-800-728-6942 or RAO@dtsc.ca.gov
Last updated: January 2, 2025
Universal Waste Links
Hazardous Waste Links
- Hazardous Waste Home
- Certified Appliance Recycler (CAR) Program
- CUPAs
- Defining Hazardous Waste
- Electronic Waste (E-Waste)
- Enforcement and Emergency Response Division
- Facilities (TSDFs)
- Generator Improvements Rule
- Generators
- Hazardous Waste ID Numbers
- Hazardous Waste Management Plan
- Hazardous Waste Manifests
- Hazardous Waste Tracking System
- Household Hazardous Waste
- Metal Recycling
- Metal Shredding Facilities and Wastes
- Permitting
- Toxics in Products
- Transporters
- Universal Waste
- Form 1358
- California Hazardous Waste Codes
Hazardous Waste Related Links
- Annual/Biennial Reports
- Annual Fee Summary
- Customer Billing Portal (Cost Recovery)
- DTSC Advisory on the Management of Spent Fuels
- EnviroStor
- Hazardous Waste Publications
- Find a Registered Hazardous Waste Transporter
- Hazardous Waste Policies & Procedures
- Hazardous Waste Project Documents
- Imports and Exports of Hazardous Waste
- Kettleman Hills Facility
- Land Use Restriction Sites
- Office of Criminal Investigations
- PV Modules (Solar Panels)
- Regulatory Assistance Office
- Report an Environmental Concern
- Retail Waste